Cable Materials
home>>products
Our Products
PESTOCHEM is cable materials supplier of cable compounfs, tapes and raw materials. We are dedicated to producing outstanding quality cable compounds under ISO9001, 14001, and 18001. We are going through a strict quality control protocol (GB/T19001 GB/T28001). Our products are exported to 23 countries in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Europe, North America and South America, and many of our customers are well-known cable manufacturers in this field.
Our Featured Compounds Product lines
1.Compounding: Silane XLPE- Production Equipment
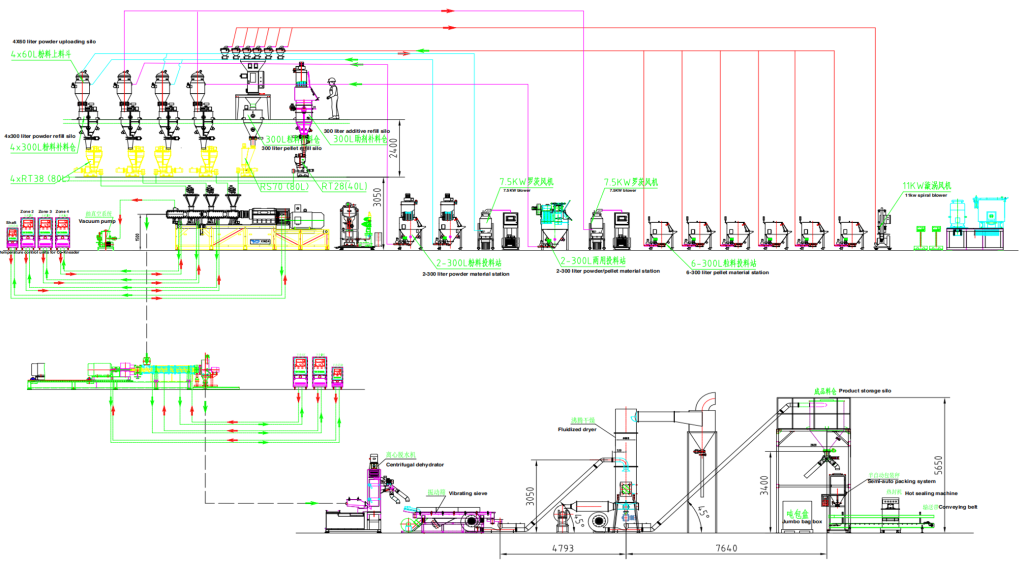
2.Compounding: Peroxide XLPE – Production Equipment
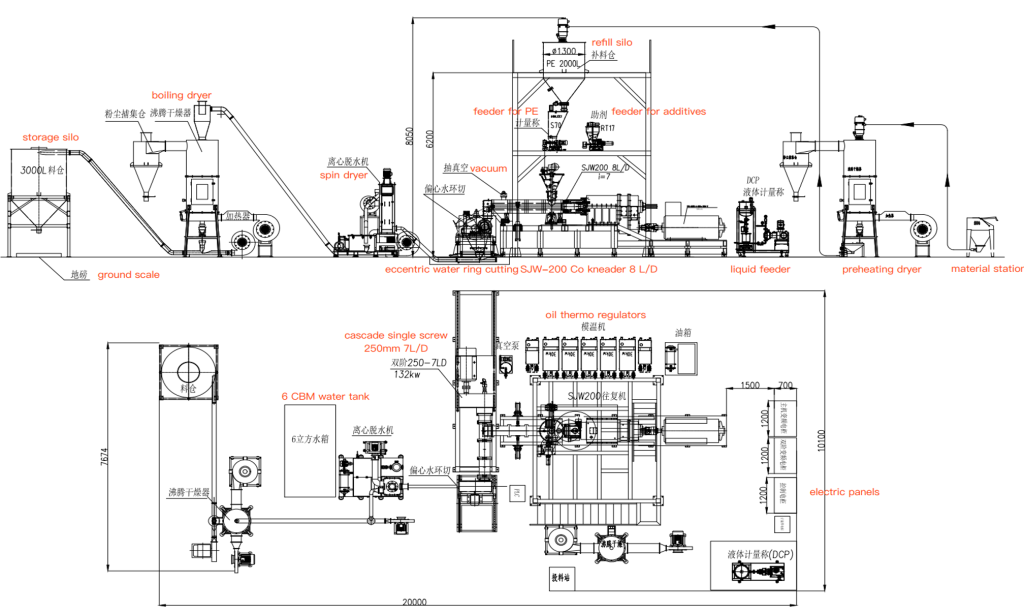
3.Compounding: Semicon- Production Equipment
FORMULA PROBLEMS ONE-STOP SOLUTION
Recommend the most suitable cable material for you
Production, packaging and transportation
- Our factory is located in Shandong, China, with complete production equipment, complete production lines, skilled workers, continuous research and development by experts, and sophisticated scientific research equipment, and is committed to providing customers with high-quality products.
- Different packaging is provided according to different products. For example, aluminum hydroxide powder (ATH), customers can choose different specifications of packaging according to needs:
- 25kg small bag, 70 bags in one pallet, pallet.
Dimension of a pallet: 1100*1300*1800mm(L*W*H) - 700kg big bag, 1 bag with one pallet
Dimension of a pallet: 1100*1100*1200mm(L*W*H)
- During the transportation process, PESTOCHEM will choose appropriate reinforcement methods to ensure that long-term sea voyages will not affect the quality of the goods.
Structure of High Voltage Power Cables——A Typical Design Example
High voltage power cables are essential components in modern power transmission systems, widely used in power plants, substations, industrial facilities, and urban distribution networks. To ensure long-term, stable, and safe operation under high voltages, these cables are designed with precise and robust multi-layer structures.
We wil take the high-voltage cable structure as an example, focusing on four key layers: conductor, insulation, screen and sheath. Each sectior explains the function and material selection of the corresponding layer, and provides technical data and standard support.
Conductor
Chapter 1
Insulation
Chapter 2
Screen
Chapter 3
Sheath
Chapter 4
Here’s a common configuration for a 110kV high voltage cable:
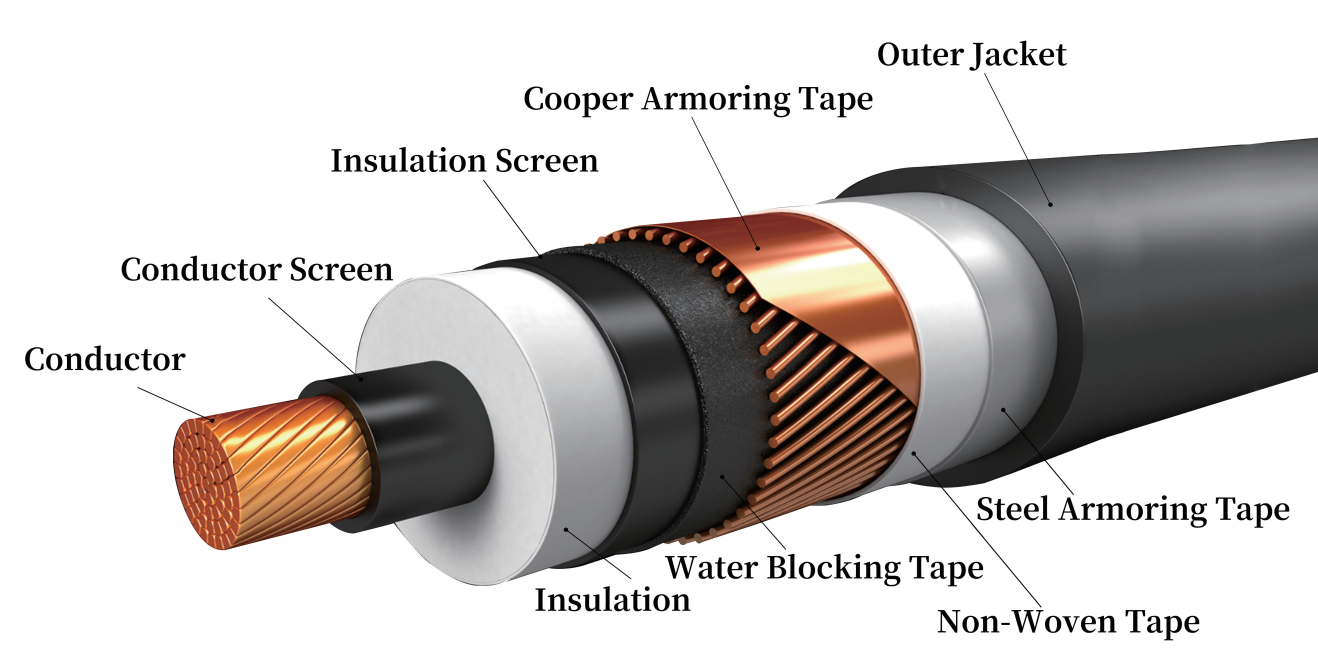
*Outer Jacket/Sheath (HDPE) → Steel Armoring Tape→Non-woven Tape→Cooper Armoring Tape→Water Blocking Tape→Insulation Screen→Insulation(XLPE, ~20mm)→Conductor Screen→Conductor
Chapter 1
Conductor: The Core Pathway for Electric Power
Function
The conductor is the main pathway for electric current within the cable. Its primary function is to transmit electricity from the power source to the load with minimal resistance and power loss. High-quality conductors improve energy efficiency and reduce thermal stress, thereby extending the cable’s operational life.
Types of Conductors
According to IEC 60228, high-voltage conductors fall into these main categories:
- Solid Conductors (Class 1)
- Single-strand copper or aluminum.
- Used in static installations.
- Stranded Conductors (Class 2)
- Made of multiple twisted strands.
- Offer better flexibility and mechanical reliability.
- Flexible Conductors (Class 5/6)
- Used in cables requiring high flexibility (rare in HV cables).
Common Conductor Materials
| Material | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | ≈5.96×10⁷ | Excellent conductivity, high strength, costlier |
| Aluminum (Al) | ≈3.5×10⁷ | Lightweight, lower cost, lower conductivity |
| Copper Alloys | Varies | Balanced conductivity and strength |
Copper conductors are most common in HV applications (≥110kV) due to their superior conductivity and stability. Aluminum is chosen in cost-sensitive or weight-critical projects such as long-distance overhead lines.
Chapter 2
Insulation: The Dielectric Barrier Against Leakage
Function
The insulation layer isolates the conductor from other conductive parts and ground, preventing leakage currents and short circuits. It also withstands the high electric fields generated by high voltage operations, making it a critical component for safety and performance.
Common Insulation Materials
| Material | Relative Permittivity | Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Thermal Stability | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XLPE | 2.3–2.5 | 20–30 | High | Excellent dielectric and thermal properties; widely used |
| EPR | 2.5–3.0 | 15–25 | Moderate | Flexible, weather-resistant, higher cost |
| PVC | 3.0–5.0 | 10–15 | Low | Economical but lower dielectric strength |
Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) is the industry standard for high voltage insulation due to its high breakdown voltage, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand continuous operating temperatures up to 90°C.
Insulation Thickness (Based on Voltage Level)
- 110kV: ~18–20mm
- 220kV: ~25mm
- 500kV: ~35mm or more
The insulation must be thick enough to prevent electrical treeing, a major degradation mechanism in HV systems.
Chapter 3
Screen: Controlling Electric Fields and Interference
Function
The screen system in HV cables has two primary roles:
- Electric Field Control: Ensures uniform field distribution, preventing field concentrations that could damage insulation.
- Electromagnetic Interference Protection: Limits the emission of electromagnetic radiation that could affect nearby systems.
Typical Screen Layers
A complete screen system typically includes:
- Conductor Screen
- Semi-conductive material applied directly over the conductor.
- Smooths the transition of the electric field into the insulation.
- Insulation Screen
- Semi-conductive layer applied over the insulation.
- Further smooths and contains the electric field.
- Metallic Sheath / Armor
- Made from copper tapes, wires, or aluminum foil.
- Provides a low-impedance path to ground and blocks EMI.
Screen Materials
| Screen Layer | Material Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Layer | Carbon black-filled PE | Smooths field transition, prevents discharges |
| Metallic Shield/ Armor | Copper tapes/wires, Al foil | Grounding and EMI containment |
The metallic screen should have resistance no greater than one-tenth that of the conductor to effectively channel leakage currents and EMI to ground.
Chapter 4
Sheath: Environmental and Mechanical Protection
Function
The sheath is the outermost layer of the cable, serving three vital functions:
- Mechanical protection
- Environmental resistance (moisture, chemicals, UV, etc.)
- Additional insulation barrier in some cases
It ensures the inner structure remains intact even in challenging conditions such as burial, moisture, or physical stress.
Common Sheath Materials
| Material | Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PVC | Low cost, flame retardant, but heat-sensitive | Indoor cabling, distribution networks |
| PE | Durable, chemical-resistant, flammable | Underground cables, wet environments |
| HDPE | High density, excellent pressure and weather resistance | Long-term outdoor or buried installation |
| LSZH | Low Smoke Zero Halogen, safe in fires | Tunnels, hospitals, transportation sectors |
| Lead | Excellent sealing, corrosion-resistant | Ultra-HV cables, chemical zones |
Additional Layers for Harsh Environments
- Inner Sheath: Protects and bonds the shielding layer.
- Armor Layer: Steel wires/tapes for added mechanical strength.
For more technical details, consider consulting the following industry standards:
IEC 60502 – Power Cables with Extruded Insulation
GB/T 12706 – Power Cables Rated 1kV to 35kV
IEEE 404 – High Voltage Cable Joints
Read More Posts

Key Cable Properties That Influence Material Selection
Key Cable Properties That Influence Material Selection Selecting the correct cable material is critical for system reliability, safety, and compliance. Poor material choices can cause premature failur

Environmental and Chemical Resistance of Wire and Cable
Environmental and Chemical Resistance of Wire and Cable Cables exposed to weather, chemicals, and heat degrade quickly. Failures caused by such degradation result in downtime, safety hazards, and cost

Flame Retardancy and Fire Safety Requirements of Wire and Cable
Flame Retardancy and Fire Safety Requirements of Wire and Cable A single spark in the wrong cable can start a fire that destroys entire systems. The loss can be huge, not just in terms of property but



