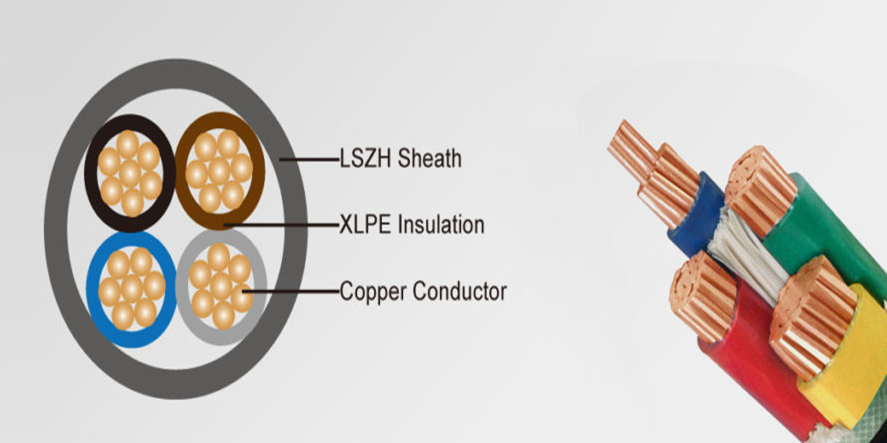
How LSZH Cables Differ from Non-LSZH Cables?
Struggling to meet fire safety codes or worried about toxic smoke from cable fires? Choosing the right compound helps protect both lives and equipment.
LSZH cables—made without halogens—reduce toxic smoke and corrosive gas emissions in a fire. This makes them safer for use in buildings, transportation, and confined public spaces. Below, I’ll break down what makes LSZH unique, how they compare to standard cables, and when you should use them.
What Are LSZH Cables and What Makes Them Unique?
Looking for safer cable options in enclosed or public environments? LSZH cables are engineered for minimal emissions under heat or flame.
LSZH stands for Low Smoke Zero Halogen. These cables use specialized polymers like EVA blends, polyethylene, or thermoplastic elastomers without chlorine, bromine, or fluorine. They incorporate flame retardants that don’t produce acidic gases or thick smoke during combustion.
Key characteristics include:
| Property | LSZH Cables | Halogenated Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Halogen Content | 0% | 20–40% |
| Smoke Output | Very low | High |
| Acid Gas Emission | <0.5% (IEC 60754) | >5% |
| Flame Retardancy | Yes (non-halogen system) | Yes (via halogens) |
| Typical Polymers | EVA, PE blends, TPE | PVC, PE |
Compliance Standards:
- IEC 60332 – Flame propagation
- IEC 61034 – Smoke density
- IEC 60754 – Halogen acid gas content
These properties make LSZH the standard for mass transit, hospitals, airports, and tunnels—anywhere fire safety matters.
What Are the Key Differences Between LSZH and Non-LSZH Cables?
Trying to understand which cable fits your project’s safety and cost goals? Here's what really separates LSZH from traditional halogenated cables.
Smoke and Toxic Gas Emissions
- LSZH cables release low smoke and non-acidic gases, preserving visibility and reducing corrosion risk.
- PVC or PE-based cables emit dense smoke and corrosive gases like HCl, which damage electronics and harm people.
| Parameter | LSZH | Non-LSZH |
|---|---|---|
| Smoke Transmission Loss | ≤150% (better visibility) | Often >300% |
| Acid Gas Emission | ≤0.5% by mass | Up to 20% |
| Toxicity | Low | High (due to HCl, Br₂) |
Fire Retardancy Mechanism
- LSZH: Uses metal hydroxides (ATH, MDH) that absorb heat and form protective char.
- Non-LSZH: Relies on halogen gases to suppress flame, but increases toxicity.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
LSZH compounds help meet modern building codes (EN 50267, RoHS), making them compliant for eco-conscious projects. Halogenated materials are increasingly restricted in Europe and some US markets.
Performance Comparison: Fire Behavior, Mechanical Properties, and Cost
Balancing safety, durability, and budget? Here’s how LSZH compares in real-world performance.
Fire Performance
LSZH passes stricter flame spread and smoke density tests:
- IEC 60332-3 (vertical bundle)
- IEC 61034 (smoke)
- IEC 60754-1/2 (acid gas)
PVC only passes IEC 60332-1, which is for single cable burn.
Mechanical Strength & Durability
- Tensile Strength: LSZH ≥10 MPa (similar to PVC)
- Elongation: LSZH ≥250%
- Flexibility: Slightly lower than soft PVC, but suitable for indoor/outdoor use
- UV Resistance: Good if stabilized
- Oil/Chemical Resistance: Slightly lower than PVC, but customizable
Cost and Lifecycle Value
LSZH compounds cost 10–30% more due to cleaner additives and compounding. However, they reduce:
- Fire damage repair
- Smoke-related system failures
- Insurance liabilities
| Attribute | LSZH | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Smoke & Acid Output | Minimal | High |
| Flame Spread | Very limited | Moderate |
| UV Resistance | Needs stabilizer | Needs stabilizer |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Lifecycle Cost | Lower in critical areas | Higher with risks |
In life-safety applications, the extra cost pays for itself in damage prevention and regulatory compliance.
Summary: Should You Choose LSZH Cables?
If your project requires:
- High fire safety
- Low smoke and toxicity
- Code compliance in public buildings or transport systems
Then LSZH cables are the smarter, safer option. For lower-risk, budget-driven installations without human occupancy, non-LSZH may still fit.
💡 Tip: Always match the cable material to your site’s fire code and equipment sensitivity level.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Are LSZH cables halogen-free in all layers?
A: Yes. LSZH cables use halogen-free insulation and jacketing. Always verify full compliance with IEC 60754 and material TDS.
Q2: Where are LSZH cables typically used?
A: Data centers, hospitals, subway systems, offshore platforms, ships, and enclosed buildings with strict fire codes.
Q3: Are LSZH cables more difficult to process?
A: Slightly. They require specialized extrusion and compounding equipment, especially to balance flame retardancy and flexibility.
Q4: Can LSZH be recycled?
A: Yes, though the process depends on the polymer base. Many LSZH compounds are thermoplastics, making recycling easier than PVC.
Need Help Choosing LSZH Cables?
We supply halogen-free insulation and jacketing compounds that meet global standards for safety-critical applications.
👉 Contact our team for custom formulations or technical datasheets.