Applications of PE Materials in Cables
Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent electrical insulating properties, low cost, and versatility. PE is commonly used in cable manufacturing for a range of applications due to its strong dielectric properties, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Below, we explore the key applications of PE materials in cables.
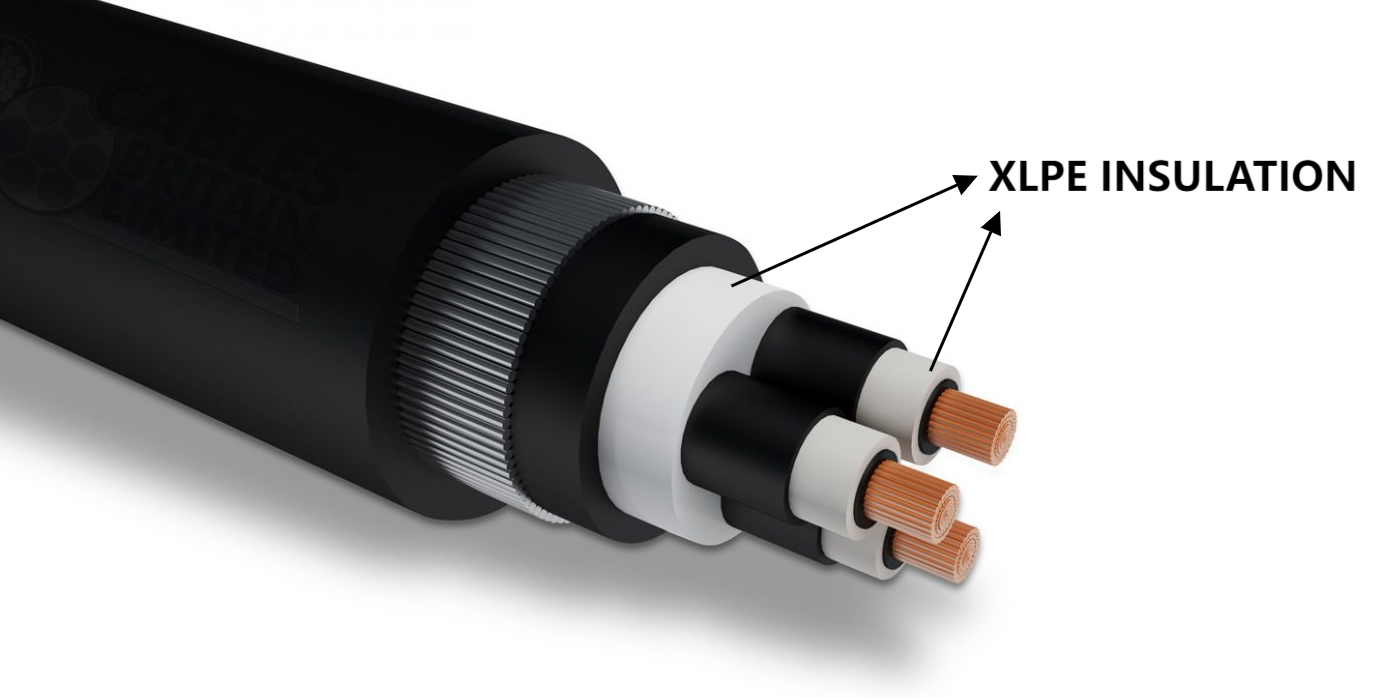
1. Cable Insulation
PE is one of the most common materials used for insulation in electrical cables, especially in low-voltage power cables, communication cables, and other types of wiring where good electrical properties are required.
Key Benefits of PE Insulation:
- Electrical Insulation: PE offers excellent dielectric properties, making it an ideal material for cable insulation to prevent electrical leakage and ensure signal integrity.
- Dielectric Strength: PE typically has a dielectric strength of around 20-30 kV/mm, making it suitable for low- and medium-voltage cables.
- Moisture Resistance: PE has very low water absorption, which makes it ideal for cables that are exposed to moisture or damp conditions.
- Water Absorption: PE has a low water absorption rate of <0.01%, ensuring stable insulation performance even in wet environments.
- Thermal Stability: PE insulation can withstand temperatures in a typical range of 40°C to +90°C, making it suitable for a variety of industrial and residential applications.
- Operating Temperature Range: PE performs well within a temperature range of 40°C to +90°C, ensuring reliable operation under typical environmental conditions.
| Property | Measurement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 20-30 kV/mm | Provides strong electrical insulation |
| Water Absorption | <0.01% | Maintains insulation integrity in moisture-rich environments |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +90°C | Suitable for typical cable environments |
2. Cable Sheaths
PE is commonly used for the outer sheath or jacket of electrical and industrial cables, offering mechanical protection against environmental factors and physical damage.
Key Benefits of PE Sheaths:
- Abrasion Resistance: PE provides good resistance to abrasion, which is essential for protecting the internal components of the cable from wear and tear.
- Abrasion Resistance: PE sheaths typically exhibit abrasion resistance levels of >1500 cycles, providing effective protection in environments with moderate physical stress.
- UV Resistance: While standard PE can degrade under prolonged UV exposure, specially treated UV-resistant PE sheaths provide long-term durability in outdoor applications.
- UV Resistance: UV-resistant PE sheaths can last up to 3000 hours of exposure without significant degradation, making it ideal for outdoor and exposed installations.
- Chemical Resistance: PE is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including oils, acids, and alkalis, making it suitable for cables used in industrial, chemical, or outdoor environments.
- Chemical Resistance: PE exhibits resistance to a variety of chemicals and solvents, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments.
| Property | Measurement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasion Resistance | >1500 cycles | Ensures mechanical protection in industrial environments |
| UV Resistance | Up to 3000 hours | Ideal for outdoor and exposed installations |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to oils, acids, alkalis | Suitable for industrial and chemical environments |
3. Low-Voltage Power Cables
PE is often used as the insulation material in low-voltage power cables, where high flexibility and reliable electrical insulation are crucial for performance and safety.
Key Benefits of PE in Low-Voltage Power Cables:
- Electrical Insulation: PE provides effective insulation for low-voltage power cables, ensuring that the current remains confined to the conductor and reducing the risk of short circuits or leakage.
- Dielectric Constant: PE has a low dielectric constant, typically between 2.2 and 2.4, which helps to minimize energy losses in cables.
- Flexibility: PE is highly flexible and allows cables to bend easily without cracking, making it ideal for installations where cables must navigate tight spaces or be subject to frequent movement.
- Flexural Endurance: PE maintains its flexibility even after exposure to high bending cycles, ensuring durability and ease of installation.
- Low Loss Factor: PE has a low loss factor, which helps to reduce energy loss during power transmission.
- Loss Factor: PE’s loss factor is typically around 0.02, ensuring minimal power loss and greater energy efficiency.
| Property | Measurement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant | 2.2-2.4 | Minimizes energy losses in cables |
| Flexural Endurance | >10 million bending cycles | Suitable for flexible power cables |
| Loss Factor | 0.02 | Ensures efficient power transmission |
4. Communication Cables
PE is commonly used in communication cables, including coaxial cables, Ethernet cables, and telephone lines, due to its low dielectric constant and excellent electrical insulating properties.
Key Benefits of PE in Communication Cables:
- Signal Integrity: PE’s low dielectric constant helps minimize signal attenuation and interference, making it ideal for high-frequency communication cables.
- Dielectric Constant: PE’s dielectric constant typically ranges from 2.2 to 2.4, which helps ensure reliable data transmission with minimal signal loss.
- Low Loss and High Efficiency: PE’s low loss factor ensures that communication cables experience minimal power or signal loss, ensuring high-efficiency performance.
- Loss Factor: The typical loss factor of PE is 0.02 at standard frequencies, reducing interference and maintaining signal quality.
- Moisture Protection: PE offers excellent resistance to moisture, ensuring that communication cables remain functional even in damp or outdoor environments.
- Moisture Absorption: PE’s moisture absorption is <0.01%, which helps maintain stable performance in wet environments.
| Property | Measurement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant | 2.2-2.4 | Maintains signal integrity in communication cables |
| Loss Factor | 0.02 | Minimizes energy loss and ensures signal quality |
| Moisture Absorption | <0.01% | Prevents performance degradation in wet environments |
5. Submarine and Underwater Cables
PE is often used in submarine and underwater cables, where its excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and pressure makes it ideal for harsh marine environments.
Key Benefits of PE in Submarine Cables:
- Water Resistance: PE provides excellent moisture resistance, ensuring that the cable remains intact and functional even when submerged in water.
- Water Absorption: PE absorbs very little water (<0.01%), which ensures the cable's longevity and reliability in underwater applications.
- Pressure Resistance: PE’s inherent strength and flexibility help it resist the high pressure found in deep-sea environments.
- Pressure Resistance: PE maintains its properties under high-pressure conditions, ensuring that the cable remains intact even at depths of several kilometers underwater.
- UV and Environmental Resistance: For cables exposed to both underwater and surface conditions, PE offers UV resistance and environmental protection.
- UV Resistance: PE sheaths used in marine cables can last up to 3000 hours of UV exposure without significant degradation.
| Property | Measurement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Water Absorption | <0.01% | Ensures long-term performance underwater |
| Pressure Resistance | High resistance to deep-sea pressure | Ensures durability in deep-sea environments |
| UV Resistance | Up to 3000 hours | Provides protection in both underwater and exposed conditions |
Conclusion
Polyethylene (PE) is a critical material in cable manufacturing, offering a wide range of benefits such as electrical insulation, moisture resistance, and mechanical strength. Its versatility makes it suitable for a variety of cable types, including low-voltage power cables, communication cables, submarine cables, and cable sheaths. PE’s excellent properties, combined with its cost-effectiveness, ensure the reliability, durability, and performance of cables in diverse environments, from residential buildings to harsh industrial and marine applications.